Injection molding has been a cornerstone of manufacturing for decades, enabling the efficient production of parts across various industries. The process is highly reliant on molds, which shape molten materials into functional and precise components. Two plate and three plate molds have been instrumental in achieving this success, with each mold offering unique advantages for different manufacturing requirements. Alongside these, the influence of complementary processes like die casting mold design has further propelled innovation in the field.
The Role of the Two Plate Injection Mold
The two plate injection mold is a fundamental tool in manufacturing, widely appreciated for its simplicity and cost-effectiveness. Its straightforward design, consisting of a cavity and core, allows for efficient production while minimizing mechanical complexity. Industries such as automotive and consumer goods rely heavily on this type of mold for producing high volumes of standardized parts. The ease of maintenance and reliability of the two plate injection mold make it an essential choice for bulk manufacturing.
Advantages of the Three Plate Injection Mold
The three plate injection mold provides advanced solutions for more complex part geometries and intricate gating systems. Its additional plate offers greater flexibility, enabling multiple gates and cleaner ejection of products. This mold type is especially useful for industries that require precision and aesthetic appeal, such as electronics and medical devices. The three plate injection mold excels in producing intricate designs, ensuring high-quality outcomes even for challenging projects.
The Impact of Automation and Digitalization
The rise of automation and digital technologies has significantly enhanced the capabilities of both two plate and three plate molds. Modern computer-aided design (CAD) software enables engineers to create optimized mold designs, while simulation tools help predict potential production issues. These advancements improve efficiency, reduce waste, and align with the growing focus on sustainability in the injection molding industry.
Sustainability in Injection Molding
Environmental concerns are driving the injection molding industry to adopt sustainable practices. Manufacturers are increasingly using recycled and bio-based plastics, alongside implementing energy-efficient processes. Both two plate and three plate molds are being adapted to meet these stringent ecological standards, contributing to a greener future. Sustainable materials and optimized techniques are essential for addressing regulatory demands and consumer preferences for eco-friendly products.
Innovations Inspired by Die Casting Mold Design
The influence of die casting mold design has brought valuable insights into the injection molding industry. Both processes share similarities in shaping materials under high pressure, leading to improvements in cooling efficiency and material flow dynamics. This cross-pollination of ideas has spurred advancements in mold design, benefiting the broader manufacturing sector. The growing integration of concepts from die casting highlights the interconnected nature of modern manufacturing.
Industry Applications of Two Plate and Three Plate Molds
The versatility of injection molding makes it indispensable across various industries. In the automotive sector, two plate and three plate molds produce lightweight and durable components such as dashboards and door panels. In healthcare, their precision is critical for manufacturing medical devices and surgical instruments. These molds are vital for meeting industry-specific demands for quality, performance, and reliability.
The Role of Additive Manufacturing
Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, is increasingly being used alongside injection molding to enhance product development. This technology enables faster prototyping and customized mold designs, complementing the strengths of traditional injection molding. By combining these technologies, manufacturers can achieve greater flexibility and efficiency, particularly for complex designs and smaller production runs.
Automation and Smart Manufacturing
Automation and robotics are transforming injection molding operations. Robots are widely used for tasks such as part removal and quality inspection, improving consistency and reducing labor costs. Smart factory technologies, powered by IoT and AI, enable real-time monitoring and optimization of production processes. These advancements are especially beneficial for complex molds like the three plate injection mold, ensuring precision and efficiency at every stage.
The Future of Injection Molding
The future of injection molding lies in adapting to emerging technologies and market demands. The continued development of sustainable materials, such as biodegradable polymers and recycled resins, will play a pivotal role in shaping the industry. Innovations in mold design and manufacturing, inspired by processes like die casting, will further enhance efficiency and versatility.
The two plate injection mold and three plate injection mold remain at the heart of modern injection molding, each offering distinct benefits. The simplicity and cost-effectiveness of the two plate mold make it ideal for high-volume production, while the precision and flexibility of the three plate mold cater to complex applications. With advancements in automation, materials, and design, the injection molding industry is well-positioned to meet future challenges. By embracing sustainable practices and innovative technologies, manufacturers can continue to drive progress and maintain their role as a cornerstone of global manufacturing.
Advancing Mold Technology: Expanding the Horizons of Injection Molding
Injection molding is a highly adaptable manufacturing process that has revolutionized industries such as automotive, electronics, consumer goods, and healthcare. Central to its success are the molds—engineered tools that shape molten materials into precisely crafted components. As manufacturers push the boundaries of innovation, two plate and three plate molds remain essential technologies, continually evolving to meet the demands of an ever-changing global market. One of the critical advantages of injection molding lies in its ability to produce parts with remarkable consistency and efficiency. The two plate injection mold is a cornerstone of this capability, widely recognized for its cost-effectiveness and reliability. Its design is straightforward yet highly functional, consisting of two main parts: the cavity plate and the core plate. This simplicity makes the two plate mold ideal for high-volume production runs, especially when manufacturing standard parts with minimal complexity. Industries requiring mass production, such as automotive manufacturing, depend on this mold type to deliver durable and consistent components while keeping costs in check.
In contrast, the three plate injection mold offers enhanced flexibility and precision. This mold type features an additional runner plate, which allows for more complex gating systems and improved part ejection. The ability to incorporate multiple gates within a single mold is particularly valuable for creating intricate parts with uniform material distribution. Industries such as medical devices and electronics, where precision and aesthetic quality are paramount, often rely on the three plate injection mold for its superior capabilities. Its adaptability has made it indispensable in applications where functionality and visual appeal go hand in hand.
Sustainability: A Key Driver of Change
As global industries face increasing pressure to adopt sustainable practices, the injection molding sector is at the forefront of these efforts. The environmental impact of traditional plastics has led to a surge in demand for eco-friendly alternatives, prompting manufacturers to explore new materials and technologies. Biodegradable polymers, recycled resins, and bio-based plastics are gaining traction as viable substitutes for conventional petroleum-based materials. Both two plate and three plate molds are being adapted to accommodate these sustainable materials, ensuring seamless integration into existing manufacturing processes. Mold designs now incorporate features that optimize material flow and reduce waste, such as advanced cooling systems and automated gating mechanisms. These innovations not only enhance production efficiency but also align with the growing emphasis on environmental responsibility.
Sustainability in injection molding also extends to energy consumption. Modern injection molding machines are designed to be energy-efficient, incorporating technologies such as servo-driven motors and precision heating systems. The combination of sustainable materials and energy-efficient machinery is setting new benchmarks for environmentally friendly manufacturing, positioning the industry as a leader in the global push for sustainability.
The Role of Additive Manufacturing
Additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing, is increasingly being used alongside traditional injection molding processes. While injection molding excels in high-volume production, additive manufacturing offers unparalleled flexibility for prototyping and small-batch production. The integration of these technologies is proving to be a game-changer, enabling manufacturers to achieve faster turnaround times and more customized solutions. In mold design, additive manufacturing allows for the creation of intricate and complex geometries that would be challenging or impossible to achieve using conventional methods. For example, conformal cooling channels—designed to optimize heat dissipation within the mold—can be produced using 3D printing. These advanced cooling systems improve cycle times and enhance the overall quality of the molded parts.
The synergy between injection molding and additive manufacturing is unlocking new possibilities for product development. By combining the strengths of both technologies, manufacturers can achieve a balance between efficiency and innovation, catering to the diverse needs of their customers.
Automation and Smart Manufacturing
The rise of automation and smart manufacturing is reshaping the injection molding industry, enhancing both productivity and quality. Automated systems are increasingly being used for tasks such as material handling, mold maintenance, and quality inspection. Robotics play a crucial role in streamlining operations, ensuring consistent performance, and reducing labor costs.
Smart manufacturing technologies, powered by the Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence (AI), are enabling real-time monitoring and optimization of injection molding processes. Sensors embedded within molds and machines collect data on variables such as temperature, pressure, and cycle time. This data is analyzed to identify potential issues, allowing manufacturers to make proactive adjustments and minimize downtime.
For complex mold designs like the three plate injection mold, these advancements are particularly beneficial. Smart technologies ensure precision and consistency, even in challenging applications, making them an indispensable part of modern injection molding operations.
Innovations Inspired by Die Casting Mold Design
The field of injection molding has benefited significantly from innovations in related manufacturing processes, such as die casting. The design principles and technologies used in die casting mold production have inspired advancements in injection molding, particularly in areas such as cooling efficiency and material flow dynamics.
Die casting molds are engineered to withstand the high temperatures and pressures associated with molten metal casting. The insights gained from designing these molds have been applied to injection molding, leading to the development of more robust and efficient mold designs. For instance, the use of advanced cooling systems and high-strength materials in die casting molds has influenced the design of injection molds, improving their durability and performance.
This cross-pollination of ideas between die casting and injection molding underscores the interconnected nature of modern manufacturing. By leveraging the strengths of multiple processes, manufacturers can achieve greater efficiency and innovation, driving progress across the industry.
Industry Applications: Meeting Diverse Needs
Injection molding is a versatile process that caters to a wide range of industries. In the automotive sector, two plate and three plate molds are used to produce lightweight, durable components such as dashboards, bumpers, and interior trim panels. The ability to produce parts with consistent quality and tight tolerances is critical for meeting the stringent performance standards of this industry. In healthcare, injection molding plays a vital role in the production of medical devices and surgical instruments. The precision and reliability of the process ensure that these products meet the high safety and quality standards required in the medical field. Both two plate and three plate molds are used to create components such as syringes, IV connectors, and diagnostic equipment, contributing to the advancement of healthcare technologies.
The electronics industry also relies heavily on injection molding for producing components such as connectors, enclosures, and housings. The three plate injection mold, in particular, is well-suited for creating intricate designs with multiple gating systems, ensuring optimal material distribution and minimal defects.
Plate or three plate molds, may be more appropriate. Despite these challenges, the 2 plate injection mold continues to be a popular choice for manufacturers due to its balance of simplicity and functionality. The cost advantages of a 2 plate mold are also significant, especially for businesses that need to produce large quantities of relatively straightforward plastic parts. The mold itself is typically less expensive to produce and maintain compared to more complex designs, making it an excellent choice for small to medium-scale production runs. The reduced costs are particularly beneficial for industries that require frequent tooling changes, as the quick turnaround and relatively low cost of 2 plate molds allow for a more agile production process.
The simplicity of the 2 plate injection mold leads to increased cycle times
Additionally, the simplicity of the 2 plate injection mold leads to increased cycle times, which is a crucial factor in industries where efficiency and speed are critical. The fewer the moving parts in the mold, the quicker the mold can be opened, injected, cooled, and ejected. This enhanced speed in the production process leads to increased output, which is particularly advantageous for businesses operating in high-demand markets. Another factor to consider when evaluating the two plate injection mold is its versatility. Despite being simple, it can be adapted to produce a wide variety of parts, including those with multiple cavities. For example, a multi-cavity two plate mold allows for several identical parts to be created in a single injection cycle, which increases overall productivity. Furthermore, the two plate mold can be designed with a wide range of materials, including various grades of plastics, to meet the specific needs of different industries.
However, one of the challenges associated with the two plate mold is the potential for limitations in the part’s design. For instance, parts with complex shapes, undercuts, or intricate features may be difficult to produce with a basic two plate mold. The parting line in a 2 plate mold also poses constraints in terms of part design, especially for components that require the inclusion of inserts, undercuts, or specialized features that demand a more complex mold structure.
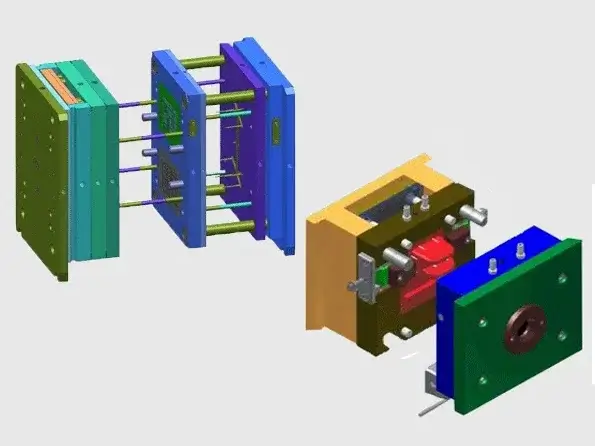
3 Plate Injection Mold
In contrast to the two plate mold, the three plate injection mold design offers a more complex and versatile option for producing plastic parts. A three plate mold, as its name suggests, consists of three primary sections instead of two: the core, the cavity, and an additional plate, known as the runner plate. This extra plate serves an essential purpose in separating the parting line of the mold, allowing for greater flexibility when producing parts with complex geometries or features that would be difficult to achieve with a two plate mold. The inclusion of a third plate in the design of a three plate mold addresses some of the limitations of the two plate mold, particularly for parts that feature undercuts, multiple cavities, or intricate details. For example, a part with a design that involves multiple components, each requiring a separate cavity, can benefit from the three plate mold configuration, as it allows for more sophisticated runner systems and part separation mechanisms. This additional complexity opens the door to a wider range of design possibilities, making the three plate injection mold a preferred choice for high-precision components with intricate features.
From a production standpoint, the three plate injection mold requires a more intricate design and, as a result, comes with higher production and maintenance costs compared to its two plate counterpart. The added complexity of the three plate mold means that it may not be the most cost-effective solution for every production run. However, it offers superior flexibility and precision when producing parts with specialized features, making it the preferred option for industries such as automotive, medical, and aerospace, where part complexity and accuracy are paramount.
In addition to offering greater design flexibility, the three plate injection mold also provides advantages when dealing with multi-material or multi-component injection molding. This capability allows manufacturers to create parts with different materials or colors within the same mold, which is particularly beneficial for producing complex or specialized components that require a combination of materials with different properties, such as hard and soft plastics or materials with different colors. While the three plate mold can address many of the limitations of the two plate mold, it does require more precise control over the injection process and can result in slightly longer cycle times. The mold design itself is more complicated and may require more careful maintenance to ensure optimal performance over time. As a result, the three plate mold is generally more suited to high-end production runs or situations where part complexity justifies the increased costs and production times.
Injection Molding Two Plate Mold
The injection molding two plate mold refers to the mold system used in the injection molding process, where two main plates—the core and the cavity—are used to shape the plastic material into the desired part. This system is the most commonly used mold configuration in the industry due to its simplicity, efficiency, and ability to handle a wide variety of plastic parts. In the two plate mold, molten plastic is injected into the cavity of the mold under high pressure. Once the plastic material cools and solidifies, the mold opens to release the finished part. The two plate mold can be used to produce a wide range of products, from small components such as caps, housings, and connectors to larger, more complex parts like automotive panels. The simplicity of the design makes it ideal for mass production, where high output and consistency are crucial.
The Future of Injection Molding
As the injection molding industry continues to evolve, several trends are shaping its future. The development of sustainable materials and energy-efficient processes will remain a top priority, driven by environmental concerns and regulatory requirements. Innovations in mold design, inspired by processes such as die casting, will further enhance the efficiency and versatility of injection molding. The integration of automation, additive manufacturing, and smart technologies is also set to transform the industry. These advancements will enable manufacturers to achieve greater precision, consistency, and customization, meeting the diverse needs of global markets.
conclusion
In conclusion, the two plate injection mold and three plate injection mold are foundational tools in the injection molding industry, each offering unique advantages for different applications. Their evolution, driven by technological advancements and sustainability goals, highlights the dynamic nature of the manufacturing sector. By embracing innovation and leveraging the insights gained from related processes like die casting mold design, the injection molding industry is poised for continued growth and success.